1. What is Macular Degeneration
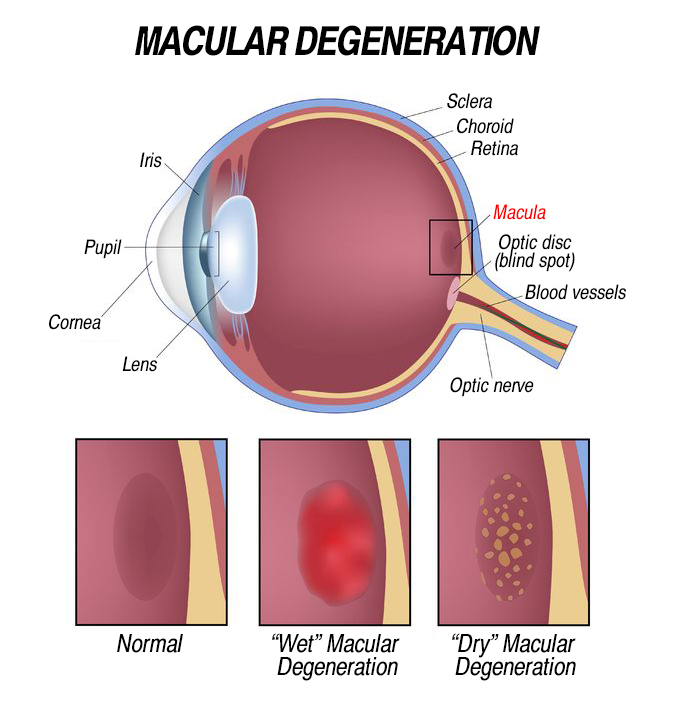
Macular Degeneration is caused by the deterioration of the central portion of the retina, the inside back layer of the eye that records the images we see and sends them via the optic nerve from the eye to the brain. The retina’s central portion, known as the macula, is responsible for focusing central vision in the eye, and it controls our ability to read, drive a car, recognize faces or colors, and see objects in fine detail.
- Dry macular degeneration (atrophic): When parts of the macula get thinner with age, some small white or yellowish deposits, called drusen, grow on the retina and beneath the macula. You slowly lose central vision.
- Wet Macular Degeneration (Neovascular): Abnormal blood vessels grow under the retina, they may leak blood or other fluids, and cause scarring of the macula. You lose vision faster than the dry macular degeneration and it is much more serious
2. Symptoms of Macular Degeneration
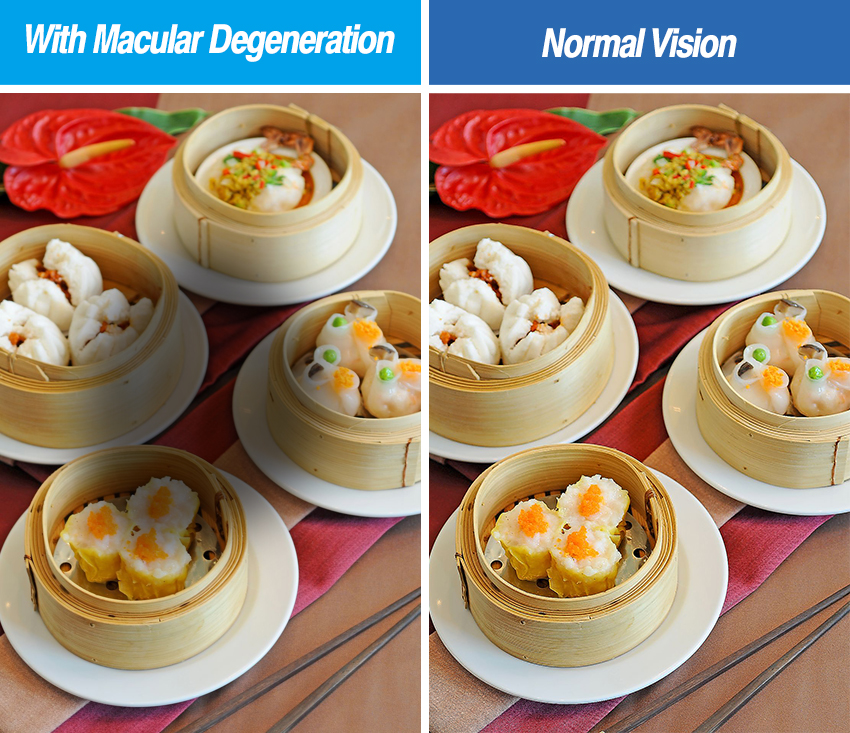
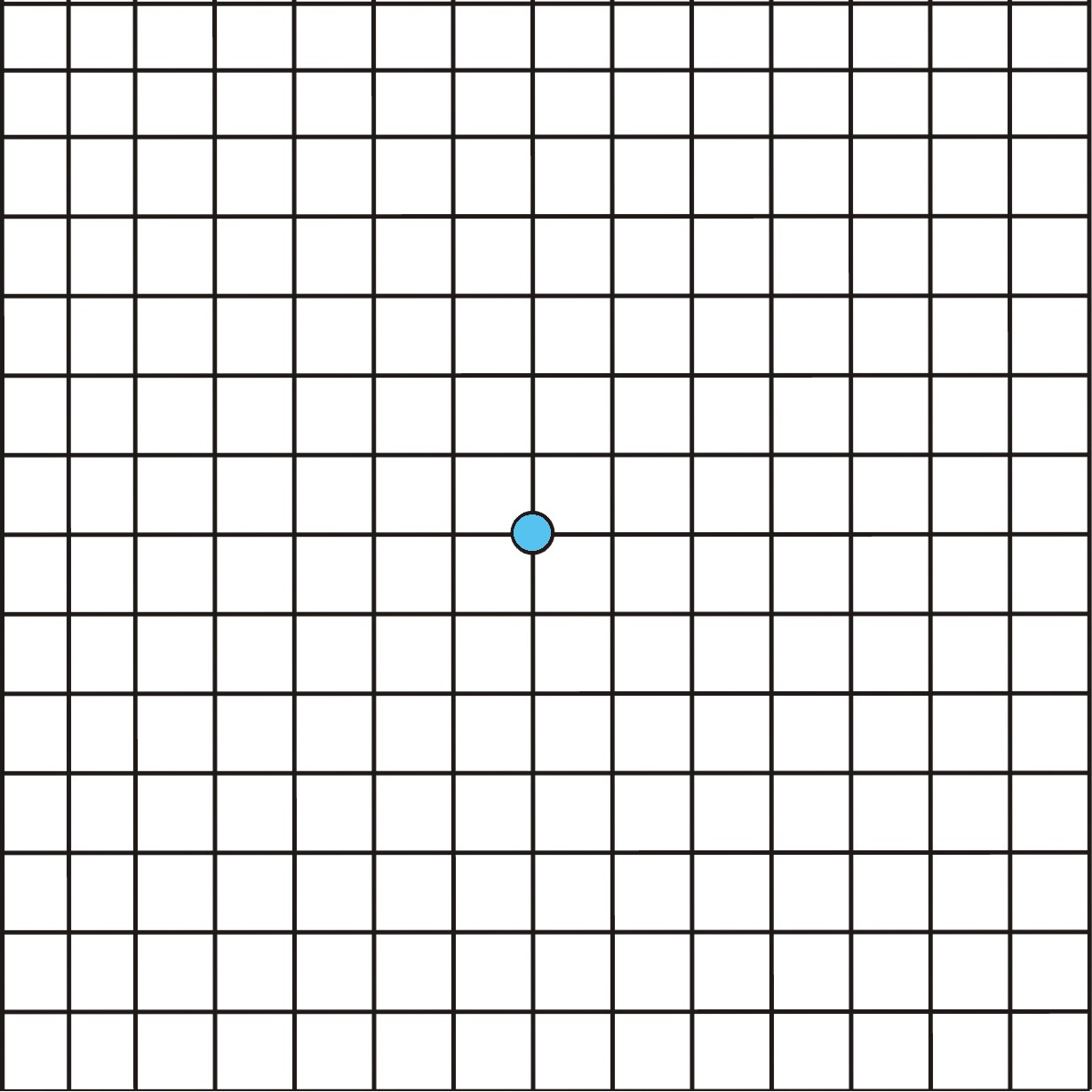
- Blurry areas appear in the center of your vision
- A change or distortion in your perception of colour, lines, blind spots
- A total loss of central visual field